Token economics play a crucial role in the success and sustainability of any blockchain project. DeBank, a cutting-edge decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, has gained significant attention in the crypto community for its innovative approach to tokenomics. In this article, we will dive deep into DeBank’s token economics model and evaluate its strengths and weaknesses.
DeBank’s token, DEB, serves as the native currency of the platform and plays a vital role in governing its ecosystem. As a utility token, DEB offers various use cases within the DeBank platform, including voting rights, staking, and governance. These functionalities not only incentivize users to hold DEB but also promote active participation and decision-making within the DeBank community.
One notable aspect of DeBank’s token economics is its deflationary mechanism. A portion of transaction fees generated on the platform is used to buy back and burn DEB tokens, reducing the total supply over time. This deflationary model creates scarcity and can potentially lead to an increase in the value of DEB tokens. Additionally, the burn mechanism ensures that DEB holders have a stake in the long-term success of the project.
Furthermore, DeBank has implemented a tiered staking system that offers additional incentives to DEB holders. By staking their tokens, users can earn rewards in the form of passive income or access to exclusive features and services. This encourages users to hold onto their DEB tokens and actively engage with the platform, fostering a strong and committed community.
However, like any tokenomics model, DeBank’s system also has its limitations. One concern is the potential concentration of voting power among large token holders. This could lead to centralization of decision-making processes and limit the influence of smaller token holders. Additionally, the success of the burn mechanism relies heavily on the platform’s ability to generate consistent transaction fees, which can be unpredictable in a volatile market.
In conclusion, DeBank’s token economics model demonstrates a thoughtful approach to incentivizing user participation and creating value for token holders. With its deflationary mechanisms and tiered staking system, DeBank aims to build a sustainable ecosystem that rewards active engagement. However, it is essential for the project to address potential concerns such as voting power concentration to ensure a fair and inclusive governance structure.
Evaluating DeBank’s token economics: An analysis
DeBank is a blockchain project that aims to revolutionize the banking industry by leveraging decentralized technology. As part of its ecosystem, DeBank has developed its own native token, with a unique set of tokenomics that govern its use and distribution.
Token Utility
The DeBank token serves as a utility token within the platform, enabling users to access and utilize various features and services. Token holders can use the token to pay for transaction fees, access premium services, participate in governance decisions, and more.
The token also functions as a means of incentivizing participation and engagement within the DeBank ecosystem. Through staking and liquidity mining mechanisms, token holders can earn rewards and benefits for actively contributing to the platform’s growth and development.
Distribution and Supply
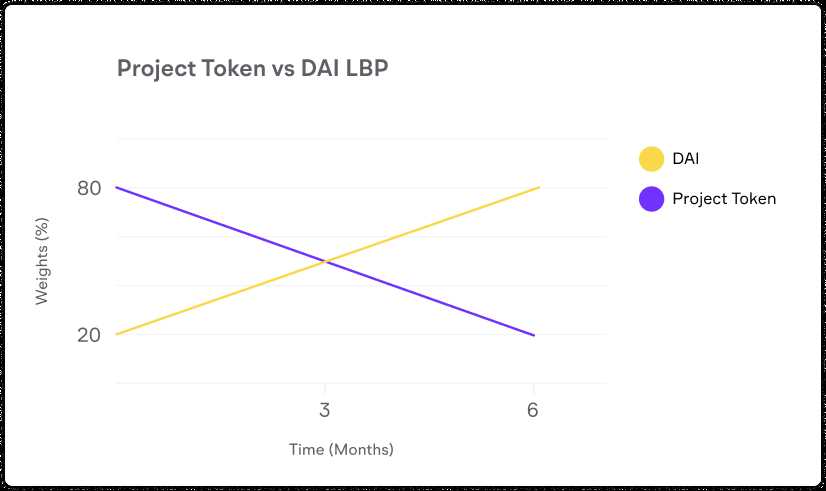
The distribution and supply of DeBank tokens are carefully designed to ensure a fair and sustainable ecosystem. A portion of the tokens are allocated for various purposes, such as project development, partnerships, marketing, and community incentives.
The team behind DeBank has also implemented a vesting schedule for token holders and team members to promote long-term commitment and prevent dumping of tokens into the market. This approach helps maintain stability and prevent market manipulation.
Furthermore, the token’s total supply is capped to prevent inflation and maintain scarcity, enhancing its value over time. This scarcity is coupled with a deflationary mechanism, where a portion of transaction fees are burned, reducing the token supply and potentially increasing its value.
Overall, DeBank’s token economics demonstrate a well-thought-out model that incentivizes user participation, ensures fair distribution, and promotes the long-term growth and stability of the ecosystem.
Understanding DeBank’s tokenomics model

DeBank has designed a comprehensive tokenomics model to incentivize participation and support the growth of its platform. The project’s native token, DEB, plays a crucial role in the ecosystem by providing various benefits and utilities.
- Staking and Governance: Holders of DEB tokens can participate in the platform’s governance by staking their tokens and voting on important proposals. This ensures a decentralized decision-making process and gives token holders a say in the project’s future development.
- Liquidity Mining: DeBank utilizes liquidity mining to encourage users to provide liquidity to its decentralized exchange. In return for providing liquidity, users are rewarded with DEB tokens. This mechanism not only incentivizes liquidity provision but also helps improve the depth and efficiency of the exchange.
- Fee Discounts: DEB token holders enjoy fee discounts when using various services and features within the DeBank ecosystem. This creates an additional value proposition for token holders and encourages them to use the platform’s services more frequently.
- Burn Mechanism: DeBank has implemented a burn mechanism to reduce the token supply over time. A portion of fees collected on the platform is regularly used to buy back DEB tokens from the market and burn them, effectively reducing the overall circulating supply. This scarcity mechanism helps maintain the token’s value and can potentially lead to price appreciation over time.
- Token Distribution: The initial token distribution of DEB was conducted through a fair and transparent token sale, ensuring a wide distribution and reducing the risk of centralization. A significant portion of the tokens was allocated to the team and advisors, with a long-term vesting schedule to align their interests with the project’s success.
This tokenomics model provides a well-balanced approach to incentivizing participation and ensuring the long-term growth and sustainability of the DeBank platform. By providing governance rights, liquidity rewards, fee discounts, and implementing a burn mechanism, DEB token holders are incentivized to actively participate in the ecosystem and contribute to its success.
The role of the token in DeBank’s ecosystem
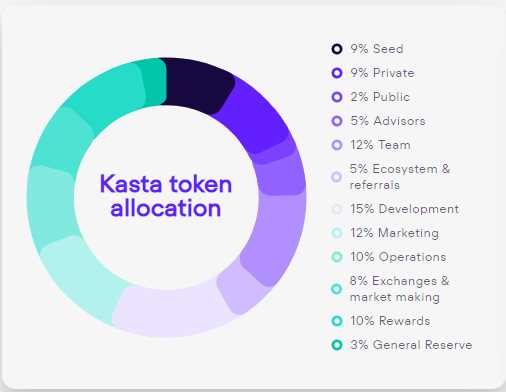
The token is a crucial component of DeBank’s ecosystem as it serves multiple important functions within the platform.
Firstly, the token acts as a medium of exchange within the platform, allowing users to transact and transfer value easily and securely. Users can use the token to pay for various services and products offered within DeBank’s ecosystem, facilitating seamless transactions without the need for traditional banking intermediaries.
Secondly, the token plays a vital role in incentivizing and rewarding users for their participation and contribution to the platform. Users can earn tokens by providing liquidity, staking their tokens, or participating in the platform’s governance activities. These rewards serve as an incentive for users to actively engage with the platform, thereby enhancing its overall growth and development.
Furthermore, the token grants users access to certain exclusive features and benefits within the DeBank ecosystem. Token holders may enjoy discounted fees, priority access to new features or products, or even access to premium content or services. This creates additional value for token holders and encourages the acquisition and retention of tokens.
The token also plays a crucial role in the governance of the platform. Token holders have the right to participate in the decision-making process by voting on important proposals and protocol upgrades. This ensures that the platform’s future direction is determined by its community, enhancing transparency, decentralization, and consensus.
Overall, the token serves as the lifeblood of DeBank’s ecosystem, enabling secure and efficient transactions, incentivizing participation, providing exclusive benefits, and ensuring community governance. Its multifunctionality adds value to both users and the platform, making it an integral part of DeBank’s success.
What is DeBank’s token economics model?
DeBank’s token economics model is a model that outlines how the project’s tokens are designed, distributed, and used within the ecosystem. It includes details on token allocation, token utility, and the mechanisms for creating value and incentivizing participation.
How are DeBank’s tokens allocated?
DeBank’s tokens are allocated in several ways. A portion of the tokens is allocated to the team and early investors as a reward for their contributions and to incentivize their continued involvement. A portion is also allocated to the community through token sales and airdrops, ensuring widespread distribution. Additional tokens may be allocated to ecosystem development, partnerships, and marketing efforts.